Version 22.07 has been released!
2023-03-14
After a long period of intense development and testing, the iNexBot control system version 22.07 has been released!
So what are the highlights of this release? Let me give you a detailed overview!
Major Feature Updates
Welding Process Revamp
The welding process has undergone a major revamp in this release, introducing numerous new functionalities.
- Added spot welding functionality
- Added circular weave in weave welding
- Added weave welding reference point instruction REFP
- Added fixed point weave welding
- Added multi-layer multi-pass welding functionality
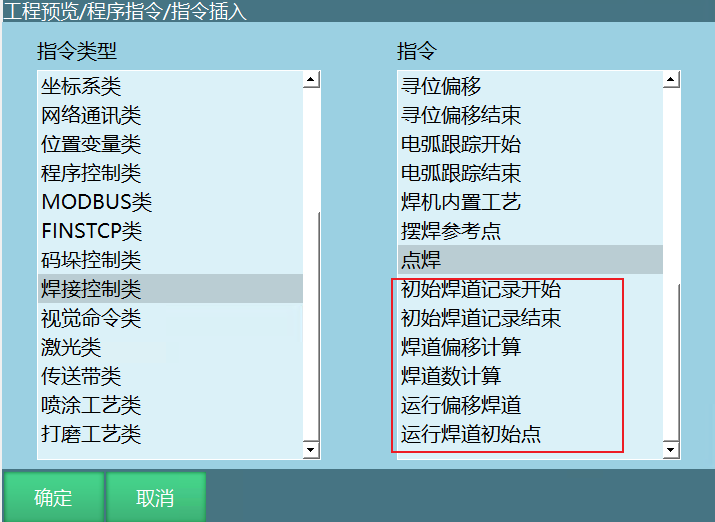
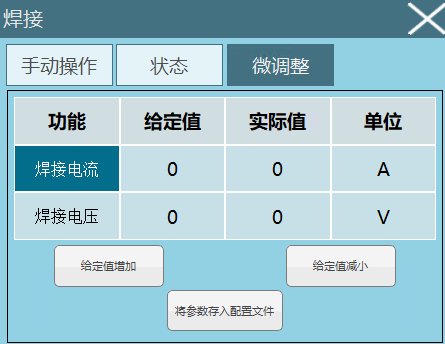
- Added welding current and voltage fine adjustment function
- Optimized restart functionality
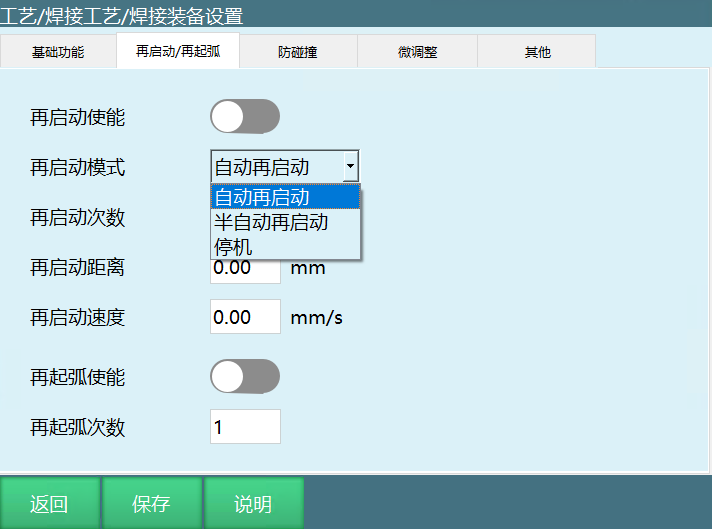
- Added arc re-ignition feature
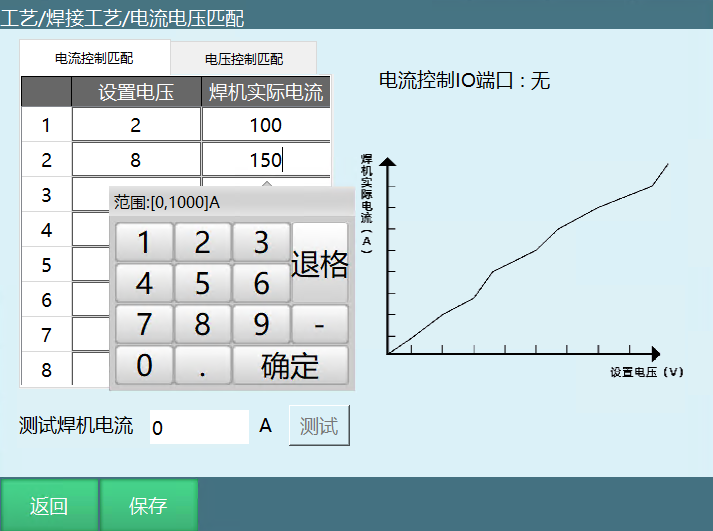
- Enhanced analog current-voltage matching
- Added gradient functionality
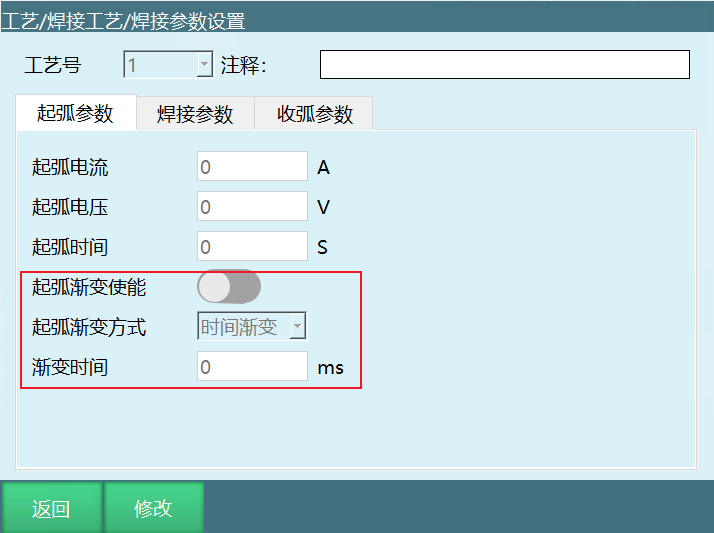
- Torch post-collision drag function, allowing for drag teaching of axes 4, 5, and 6 after collision
- Added automatic correction function for weave welding trajectory
Gantry Instruction
Added gantry instruction, the test data is as follows
Test environment:
4-axis SCARA robot
| Parameter | Data |
|---|---|
| Joint Speed | 5000 |
| Instruction Speed | 5000 |
| PL | 5 |
| Global Speed | 100% |
| Acceleration | 15 |
| Deceleration | 15 |
| Min Acceleration Time | 0.02 |
Test results: When the joint speed is 5000 RPM, the cycle time is 0.3s When the joint speed is 6000 RPM, the cycle time is less than 0.3s
Support for Lua
You can write more complex running logic through Lua!
Added Lua file invocation instructions to the job program
- Supports Lua 5.2
- Supports extensions written in Lua language
- Supports functions such as operating variables, IO, tool hand parameters, user coordinate parameters, error reporting, and log printing
You can also execute Lua statements separately within the job program.
Current Line Execution Functionality
You can select any line of instruction and run the instructions from the current line, significantly improving debugging efficiency.
Variable Binding for Instruction Parameters
Now the parameters in instructions can be bound to variables, which can significantly reduce programming workload and enable more complex logic!
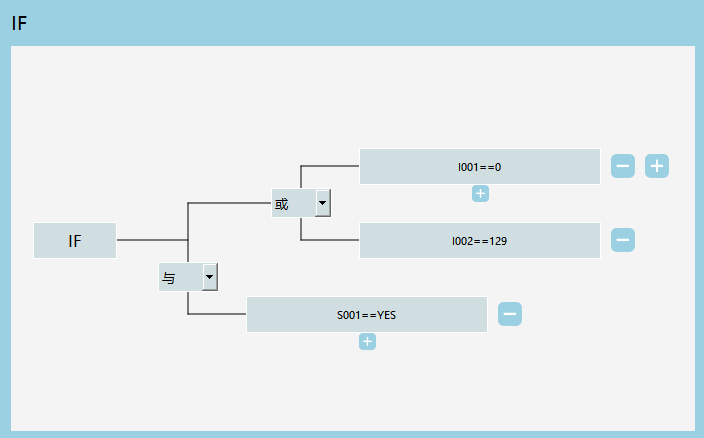
Multi-Condition Judgment
The conditional judgment instruction (IF) now supports multi-condition judgment and provides a user-friendly interface. You can easily write judgment instructions with complex conditions.
Here's an example of an IF instruction with the condition IF((I0010||I002129)&&S001=="YES")
New Error Reporting Mechanism
The redesigned error reporting mechanism makes error alerts more prominent and enhances overall operational safety. All errors must be cleared before the program can be run.
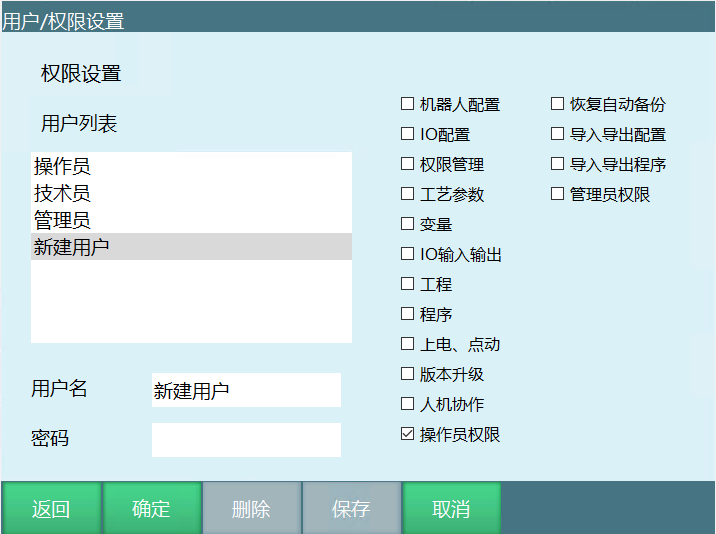
User Permission Customization
Support for adding users with customizable permissions
Modbus Master Functionality
Added Modbus master functionality
Supports read/write operations for 4x, 3x, 4x-bit, 3x-bit, 0x, 1x address types
In any mode, Modbus can read global values
Multiple master connections are supported for Modbus, with a maximum of 9 master devices concurrently connecting to Modbus slaves
100 GP variables added to modbus
External Buttons for Collaborative Robots
Added external button function in human-machine collaboration
The following functions can be controlled through the buttons located at the end of the collaborative robot:
- Recording drag trajectory
- Playback drag trajectory
- Switching drag modes
- Power on/off
- Gripper switch
- Saving trajectory
String Type
- Added string variable class The variable interface and monitoring interface have added entry points for modifying and viewing string variables String variables are prefixed with 'S'
- Added string append instruction STRING-SPELL Supports string + operation
- Added string index interception instruction STRING-SLICE Allows for intercepting a desired portion of a string by specifying the index
- Added string separator splitting instruction STRING-SPLIT Allows for splitting a string into multiple segments by specifying the delimiter character
- Added string position query instruction STRING-LOCATE Retrieves all occurrences of a specified character in a string
- Added string length instruction STRING-LENGTH Retrieves the character length of a specified string variable
- Added string-to-non-string conversion instruction STRING-TO Can convert string variables to integer, float, or boolean variables
- Added non-string-to-string conversion instruction TO-STRING-Non Can convert integer, float, or boolean variables to string variables
- Added support for string type in multiple instruction parameters, such as output messages, Modbus read/write, network communication, etc.
Trial Run Feature
Added the trial run feature, which allows for continuous execution of instructions in teach mode.
Minor Changes
Program Editing
Optimized operation pop-up buttons to reduce steps and improve efficiency for high-intensity programming
Batch operations now support modifying process numbers
Conveyor Tracking
- Added wait points Allows for waiting at a specified point when there are no workpieces
- Added the instruction CONVEYOR_POS to obtain the conveyor belt tracking position Get the target point of this tracking and save it to the position variable
- Added conveyor belt tracking target deletion instruction CONVEYOR_REMOVE You can delete the current tracking target or all tracking targets in the queue
- Added parameter "Tracking target height"
- Added parameter "Conveyor position mode"
- Added constant speed mode The conveyor belt speed can now be obtained from the encoder or entered directly
- Parameters such as "Conveyor speed" and "Conveyor calibration value" are open and modifiable
Interference Area Robot Range Merging
- Changed to 2-point calibration of interference space
- State output, stoppable
IO Setting
- Interface UI adjustment
- The error prompt feature has been enhanced with support for different error types
- IO display with customizable names
Vision
- The vision system has been enhanced with the capability to clear the calibrated gripping attitude
- Conveyor belt visual tracking of the entire trajectory
- Added camera calibration


